| Ward | Paeditric ICU | D.O.B/Age | 11/03/2020 |
| Consultant | Prof G. vd Watt |
Abnormal result
Elevated propionic acid in the urine organic acid profile.
Presenting complaint
Fever with LRTI. ?COVID
History
Normal birth with no antenatal problems
#RVD exposed
Now:
#FTT
#LRTI. ?COVID
The patient presented with fever and LRTI which resolved after 3 -4 days of antibiotics. The patient then developed seizures with apnoeic attacks. The patient required intubation and ventilation and was transferred to ICU. The patient was noted to be having breakthrough seizures despite anticonvulsant therapy.
Further questioning revealed that the patient had become progressively drowsy with poor feeding.
Family history: No siblings noted to have had previous problem.
Examination
The patient was noted as not interacting with his environment.
CNS exam: Low GCS with upper motor neuron signs.
Other systems unremarkable.
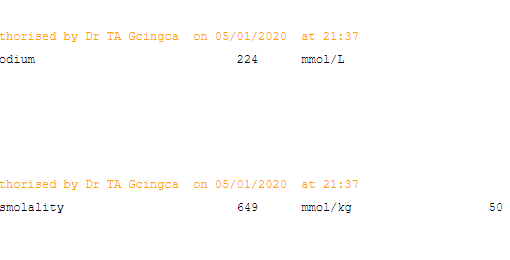
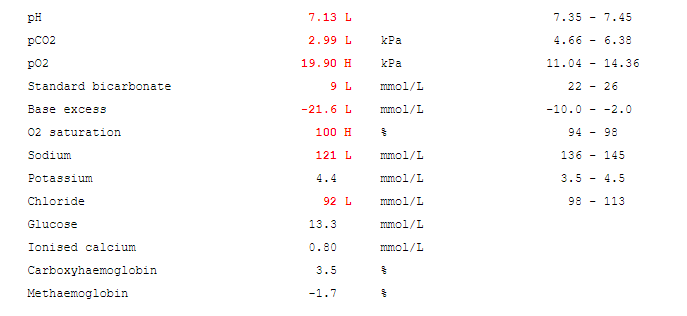
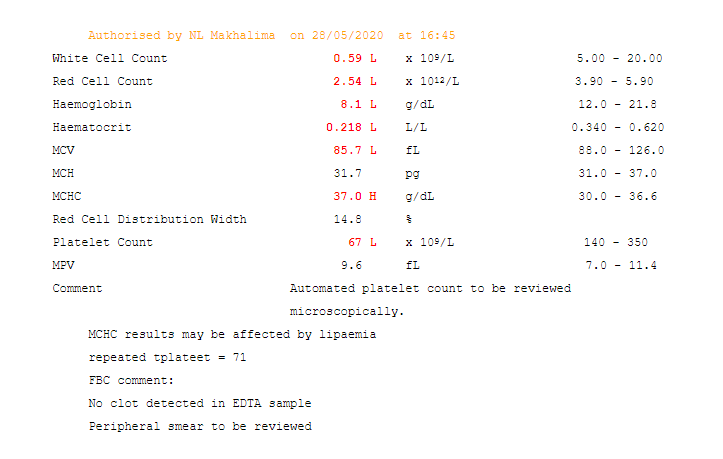
Laboratory investigations







Other investigations
CT brain may be useful in assess for organic neurological cause.
Final diagnosis
Propionic acidaemia.
DDx: Biotinidase deficiency
Take-home messages
Propionic acidaemia is an organic acidaemia characterized by deficiency of propionyl-CoA carboxylase. Propionyl-CoA carboxyalse converts propionyl-CoA to methylmalonyl-CoA. It is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. The metabolism of isoleucine, valine, threonine, and methionine produces propionyl-CoA. To a lesser degree, cholesterol and odd-chain fatty acids also contribute to propionyl-CoA levels. Affected individuals must follow a low-protein diet and early diagnosis improved prognosis.
The accumulation of propionyl-CoA results in significant mitochondrial CoA trapping and inhibited fatty acid oxidation. The enhanced anapleurosis of propionate and CoA trapping alters the pool sizes of tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) metabolites. This explains the marked hyperammonaemia that patients present with as well as potential hypoglycaemia
A high index of suspicion is required to diagnose inborn errors of metabolism (IEM). This case highlighted the importance of understanding key points in metabolic pathways. It also emphasized the correlation between catabolic stress being an initiating event in IEMs.